The TextView view is used to display text to the user. This is the most basic view and one that you will frequently use when you develop Android applications. If you need to allow users to edit the text displayed, you should use the subclass of TextView, EditText, which is discussed in the next chapter.
When you create a new Android project, Android Studio always creates the
content_main.xml file (located in the res/layout folder), which contains a
<TextView> element:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"/>
</LinearLayout>
NOTE: In some other platforms, the TextView is commonly known as the label view. Its sole purpose is to display text on the screen.
TextView Attributes
Following are the important attributes related to TextView control. You can check Android official documentation for complete list of attributes and related methods which you can use to change these attributes are run time.
| Attribute |
Description |
| android:id |
This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control. |
| android:capitalize |
If set, specifies that this TextView has a textual input method and should automatically capitalize what the user types.
- Don't automatically capitalize anything - 0
- Capitalize the first word of each sentence - 1
- Capitalize the first letter of every word - 2
- Capitalize every character - 3
|
| android:cursorVisible |
Makes the cursor visible (the default) or invisible. Default is false. |
| android:editable |
If set to true, specifies that this TextView has an input method. |
| android:fontFamily |
Font family (named by string) for the text. |
| android:gravity |
Specifies how to align the text by the view's x- and/or y-axis when the text is smaller than the view. |
| android:hint |
Hint text to display when the text is empty. |
| android:inputType |
The type of data being placed in a text field. Phone, Date, Time, Number, Password etc. |
| android:maxHeight |
Makes the TextView be at most this many pixels tall. |
| android:maxWidth |
Makes the TextView be at most this many pixels wide. |
| android:minHeight |
Makes the TextView be at least this many pixels tall. |
| android:minWidth |
Makes the TextView be at least this many pixels wide. |
| android:password |
Whether the characters of the field are displayed as password dots instead of themselves. Possible value either "true" or "false". |
| android:phoneNumber |
If set, specifies that this TextView has a phone number input method. Possible value either "true" or "false". |
| android:text |
Text to display. |
| android:textAllCaps |
Present the text in ALL CAPS. Possible value either "true" or "false". |
| android:textColor |
Text color. May be a color value, in the form of "#rgb", "#argb", "#rrggbb", or "#aarrggbb". |
| android:textColorHighlight |
Color of the text selection highlight. |
| android:textColorHint |
Color of the hint text. May be a color value, in the form of "#rgb", "#argb", "#rrggbb", or "#aarrggbb". |
| android:textIsSelectable |
Indicates that the content of a non-editable text can be selected. Possible value either "true" or "false". |
| android:textSize |
Size of the text. Recommended dimension type for text is "sp" for scaled-pixels (example: 15sp). |
| android:textStyle |
Style (bold, italic, bolditalic) for the text. You can use or more of the following values separated by '|'.
- normal - 0
- bold - 1
- italic - 2
|
| android:typeface |
Typeface (normal, sans, serif, monospace) for the text. You can use or more of the following values separated by '|'.
- normal - 0
- sans - 1
- serif - 2
- monospace - 3
|
Example
This example will take you through simple steps to show how to create your own Android application using Linear Layout and TextView.
You will use Android studio to create an Android application and name it
MyApplication under a package
akraj.snow.app as explained in the
Getting Started With Android Programming chapter.
Following is the content of the modified main activity file
src/akraj.snow.app/MainActivity.java. This file can include each of the fundamental lifecycle methods.
package akraj.snow.app;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
}
}
You can set TextView from
MainActivity.java :-
textView.setText("www.androidlearning.in");
Following will be the content of
res/layout/activity_main.xml file −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="@string/text"
android:textColor="@android:color/holo_blue_dark"
android:textColorHighlight="@android:color/primary_text_dark"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="40sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
Following will be the content of
res/values/strings.xml to define two new constants −
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My Application</string>
<string name="text">androidlearning.in</string>
</resources>
Following is the default content of
AndroidManifest.xml −
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="akraj.snow.app">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Let's try to run your
MyApplication example. I assume you had created your
AVD while doing environment setup. To run the app from Android studio, open one of your project's activity files and click Run

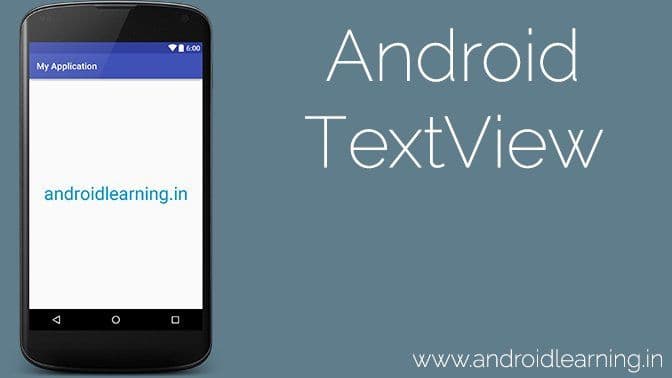
icon from the toolbar. Android studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display following Emulator window −

 icon from the toolbar. Android studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar. Android studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display following Emulator window −

 icon from the toolbar. Android studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display following Emulator window −
icon from the toolbar. Android studio installs the app on your AVD and starts it and if everything is fine with your setup and application, it will display following Emulator window −